It is always a challenge to prepare for future trends in cybersecurity. Patch management is a vital component for maintaining a solid defense. A good Patch Management System recognizes risks or weaknesses in operational software that cause an interruption of workflow.
Most IT companies focus on patch management as an update strategy for their software. Patch management is IT experts’ coordination of processes and procedures to execute software upgrades and bug fixes.
These upgrades are vital for cybersecurity and MSP services to guarantee a company’s IT infrastructure has the most up-to-date security features. This blog highlights that one must choose an appropriate ConnectWise Automate Patch Management system well-suited for one’s environment.
These systems play an essential part in protecting digital properties and developing an effective cyber security plan.
What is Patching?
What do you Know About Patch Management?
Patch management is a comprehensive process encompassing patch organization, selection, and application.
Patching is only a small part of it, as it incorporates the entire process of ensuring the security and proper functioning of the IT systems.
These include classifying applications, software, and operating systems vulnerable to cyberattacks and malfunctioning and selecting and testing optimal patches for applications.
Moreover, it has some essential features which may be slightly different from each other, depending on the environment. Like, MSPs have their own way, while other IT specialists handle it their own way.
For example, standalone systems (that run by macOS or Windows) automatically search the updates for patches and install them.
A system usually installs an update after locating one, requiring a user to restart his computer for the changes to become effective.
However, patching a system in larger organizations requires some specific steps. Software versions should not be consistent among companies if individual PC owners handle the updates of each of them separately.
MSPs typically deploy a patch management server that pushes out updates to every computer in the environment. The server performs a scan on hardware devices for any missing patches that will be administrated based on the network’s patch management policies.
Benefits or Importance of Patch Management to Know
Many big software companies regularly release patches for critical reasons. These are:
1. Security Enhancement:
2. Compliance Requirements:
3. Adding New Features:
4. Risk Mitigation and Bug Fixing:
5. Stability and Performance:
Demerits of Patch Management
- Downtime: Patch installation sometimes requires system reboots, resulting in temporary downtime. This can be troublesome for organizations that must be available around the clock.
- Compatibility Obstacles: Patches may cause compatibility issues with current software or hardware in certain cases. Careful testing is necessary to guarantee that changes do not affect routine operations.
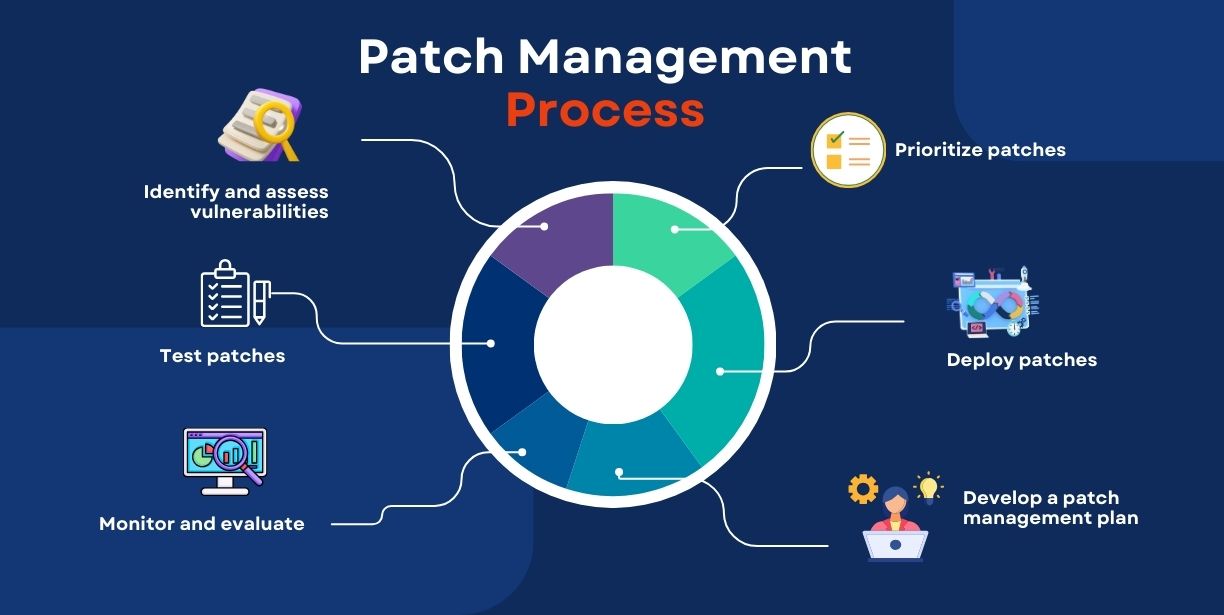
How does patch management work? (Steps Involved)
Look at Every Detail Closely
Find the Problems
Test it Out
Put the Patches in Place
Get Regular Reports
Make Patches as Required
Why do businesses prefer hiring a patch management service?
Patch management is necessary, although it is outside the scope of usual business or office tasks. Even though it is an extra task beyond regular business affairs, it requires significant time and resources. This is the main reason why many businesses choose to outsource patch management to a reputable service provider.
A patch management service provider, such as ConnectWise Automate patch management, has the tools, software infrastructure, and experience required to complete the whole patch management process.
Moreover, they update you with detailed reports on completed tasks, applied patches, bug fixes, and updates.
Why Patch Management is Important for MSPs?
Keeping your client’s software up to date and secure is an essential step in ensuring the security of their online systems. With careful preparation, MSPs may make a significant difference in safeguarding the clients’ networks.
Patch management is essential for MSPs, especially in sectors with strict regulations. Government and business entities in sensitive industries like banking and healthcare demand that enterprises adopt cutting-edge software. Updating software with the newest security features in these patches reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks.
